


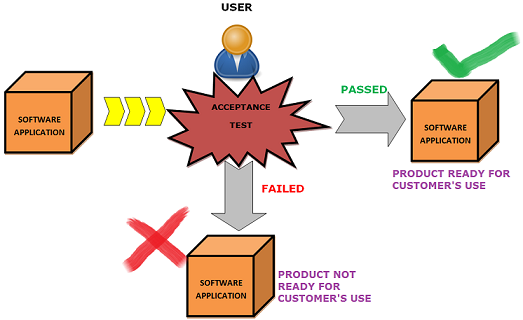
The main goal behind acceptance testing is to check whether the developed software product passes the acceptance norms defined on the basis of user and business requirements, so as to declare it acceptable or non-acceptable for its use by the users. Acceptance testing is one of the last types of software testing performed over a software or application. It is conducted by a pool of targeted users to ensure the readiness and quality of the system from user's perspective, which allows the team to meet their needs and expectations.
Acceptance testing is also referred to as red box testing. Additionally, the acceptance tests are derived from the user story and are based on the acceptance criteria, which are defined on the basis of the following:
Broadly, there are two main types of Acceptance Testing
It is an on-site acceptance testing executed at developer's site usually by the group of skilled testers. This is carried out at the end of the software development process and before the handing over of the software product to clients/users. The feedback or the collected result from the alpha testing is significantly used to fix bugs or defects, and it is feasible to improve the usability of the product.Explore more of this testing in our article Alpha Testing.
Explore more of this testing in our article Alpha Testing.
Also known by the name field testing, Beta Testing is an off-site acceptance testing, carried out at client's site by the stakeholder or the end-users. This testing involves the evaluation of the software in the real environment by its potential users before its actual release in the market.
Apart from above, acceptance testing can also be classified as under:

When a software is under testing, there are numerous components that are required to be cross-checked by the team to ensure the accuracy of the expected result as well as to validate the quality of the various features and components of the software, which automatically convince the user to accept the system. Acceptance testing plays this important role in software testing and ensures that the software delivered to the client and user is up-to-the-mark and performs as intended. Few of the other reasons for executing acceptance testing are:
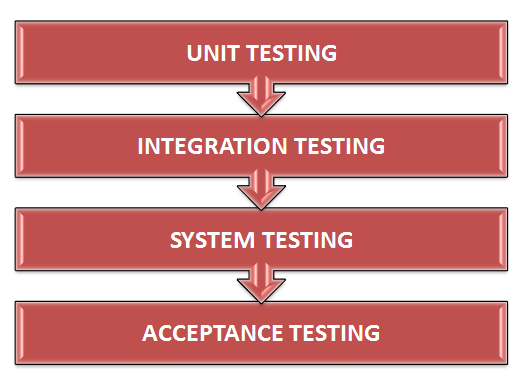
A software product goes through numerous stages of testing, before it is ready for its go-live or implementation. Likewise, before executing the testing process for acceptance testing, the team implements various techniques, like "unit testing", "integration testing", and "system testing" to assess the quality and reliability of the software. Though, this type of testing begins with the completion of system testing and before the deployment of software product for its actual use, it can also be applied to other levels, like in smoke testing, which ensures the acceptance of the software build based on its stability for further testing.
Before implementing the process of testing, it is important for the team to accumulate all the necessary components and elements, which will allow them to execute the process of testing without any hassle and will help them get accurate and expected test results. From validating the process of development to ensuring the availability of various reports and logs, everything should be present while executing acceptance testing to enhance its quality. Therefore, here is a list of various prerequisites required for acceptance testing:
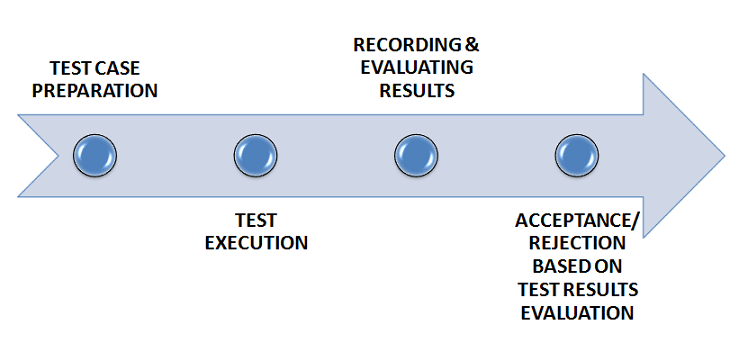
Acceptance is a formal type of testing, which follows the black-box testing strategy to execute tests on software product. It means that the testing process for acceptance testing is performed without having any prior knowledge of the software's internal working and involves feeding of inputs to observe and evaluate the response of the system. Generally, this type of testing involves multiple executions of test cases including following activities.

It is expected from every software product that it should function based on the needs of the end users to meet and satisfy their desired demands & expectations, and which can be guaranteed through acceptance testing along with gain of confidence in its user-acceptance, prior to its market release.
You can also check our next article on acceptance testing vs system testing here.
Advertisement: